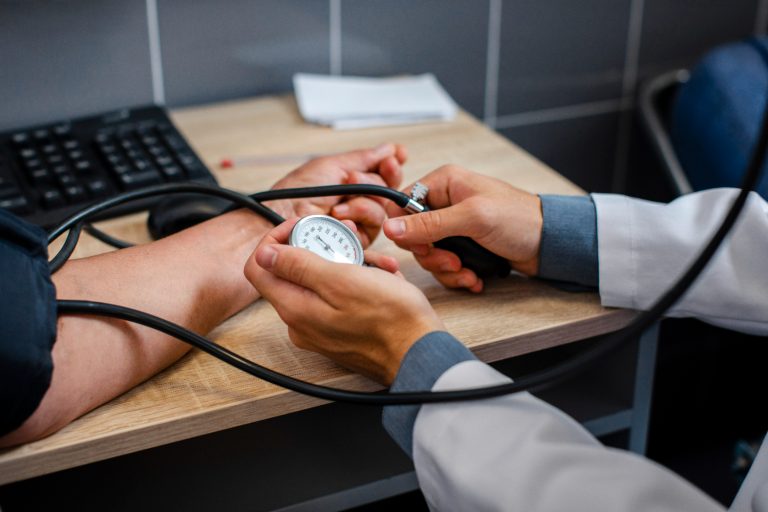
Arterial hypertension or hypertension is the most common chronic disease of the cardiovascular system in the adult population. It is characterized by a periodic or persistent increase in blood pressure.
Arterial hypertension is an insidious disease. For a long time it can proceed practically without pronounced symptoms. In the case of long-term arterial hypertension, the human body gradually adapts to high blood pressure and the patient’s well-being may remain good. However, lesions of the arteries and vital organs cannot be avoided. Here are just some of the changes that occur in the human body with hypertension:
- vessels narrow, vessel walls lose elasticity;
- vision deteriorates;
- there is a violation of the heart rate, more often in the direction of increase (tachycardia);
- due to the increased load on the heart increases the muscle mass of the left ventricle of the heart, worsens its blood supply;
- atherosclerosis of the aorta (the main artery of the human circulatory system), brain vessels, heart (coronary), etc. rapidly develops;
- load on the kidneys increases, which can lead to a violation of the main function of urinary excretion.
Risk factors
The main role in the occurrence of arterial hypertension is played by risk factors, without which the appearance of the disease is unlikely. Among the main predisposing causes are distinguished:
– Age (men over 55 years old, women over 60 years old);
– family history (development of arterial hypertension in parents, early menopause);
– smoking (including smoking cessation during the last year);
– high level of lipids in the blood;
– sedentary lifestyle;
– abdominal obesity (waist circumference greater than 88 cm for women and greater than 102 cm for men). Obese people have a 5 times higher risk of developing hypertension compared to those whose weight is normal. If your own weight is more than normal for many years, your heart and blood vessels are under severe strain;

– excessive salt intake (more than 5 g per day). Sodium is able to retain water in the body;
– chronic stress.
The danger of hypertension lies in its prolonged asymptomatic or asymptomatic course. In most cases, blood pressure rises asymptomatically, and hypertension is detected only during objective examination of the patient.
Main symptoms of arterial hypertension
- Periodically develops pressing or throbbing headaches (more often in the morning, in the occipital region, as a squeezing head hoop, the symptom increases when tilting the head downward).
- Flickering of flies or fog before the eyes, dizziness.
- During physical activity, palpitations and shortness of breath are noted.
- As the disease progresses – decreased memory, impaired concentration, impaired performance.
- Sometimes the appearance of edema of the lower extremities.
Ways to control blood pressure and prevent hypertension
In this article, we will look at some effective ways to control blood pressure and prevent hypertension.
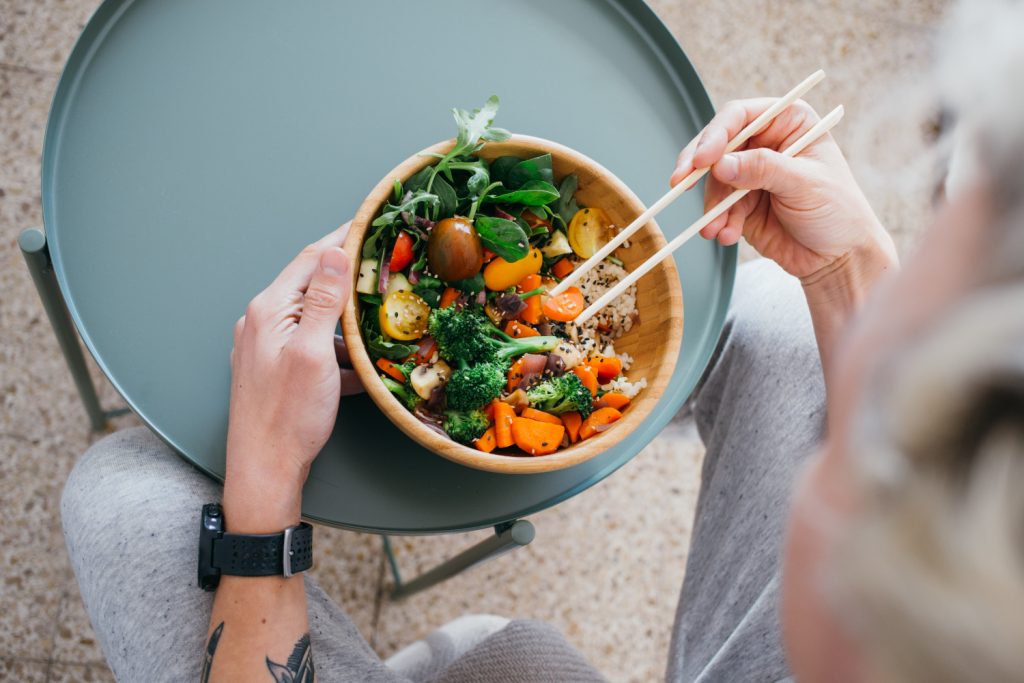
- Follow a healthy lifestyle
It plays an important role in controlling blood pressure. Your diet should be rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grain products, low-fat dairy products and low in salt. Limit your intake of saturated fats and avoid trans fats, which are often found in convenience foods, i.e. fast food or convenience foods. Engage in regular physical activity such as walking, swimming or aerobics to maintain a healthy weight and strengthen your cardiovascular system.

- Limit alcohol consumption and stop smoking
Alcohol consumption and smoking are risk factors for arterial hypertension. Try to limit your alcohol intake or stop drinking altogether. Smoking, on the other hand, negatively affects the circulatory system and can increase blood pressure. If you smoke, seek help from a cardiologist to quit the habit.
- Watch your weight
Being overweight is one of the risk factors for arterial hypertension. Try to maintain a healthy weight according to your height and physical activity. If you are overweight, reduce it gradually through a combination of a balanced diet and regular physical activity. Moderate weight loss can significantly reduce the risk of developing hypertension.
- Keep an eye on your stress levels
Chronic stress can lead to high blood pressure. Therefore, it’s important to find ways to manage stress. Practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help you reduce stress levels and maintain a healthy heart.
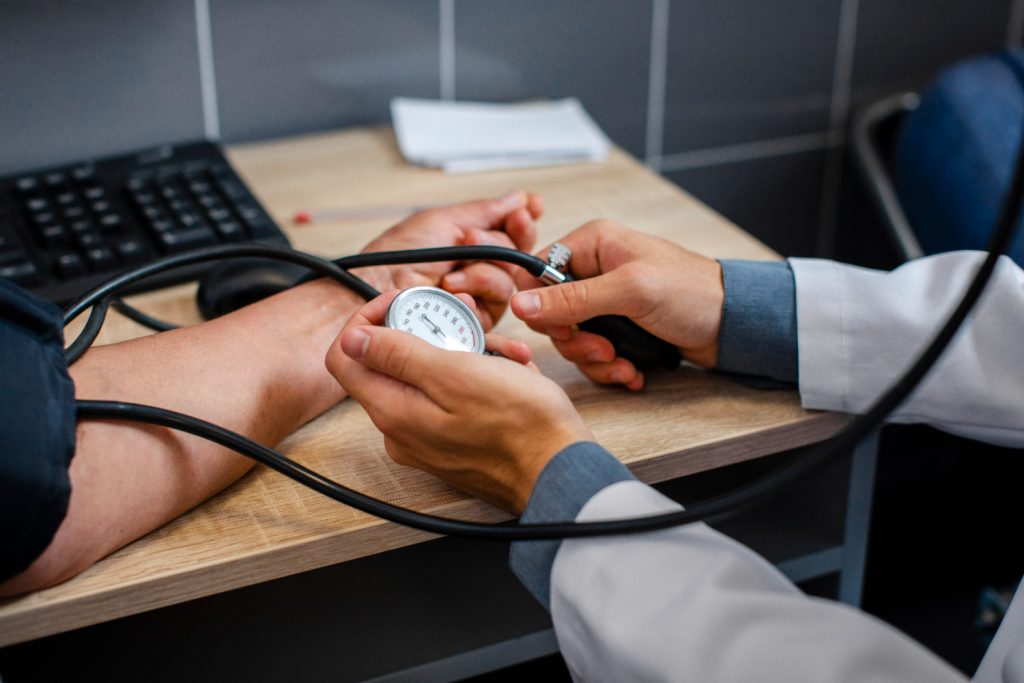
- Take your blood pressure regularly
It is important to monitor your blood pressure, especially if you have risk factors for arterial hypertension or have already been diagnosed with high blood pressure. Measuring your blood pressure regularly will help you monitor your blood pressure levels and take timely action if it starts to rise. You can use portable tonometers to measure your blood pressure at home or visit your doctor regularly for monitoring.
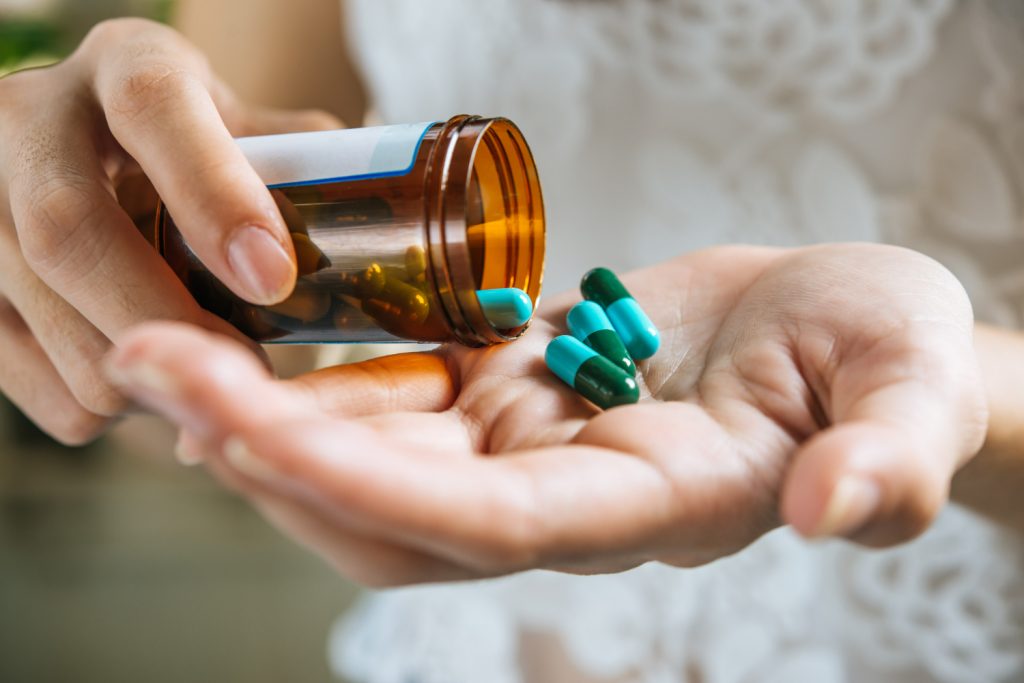
- Keep track of your medications
If you are prescribed blood pressure medication, follow your doctor’s instructions and take it regularly. Do not stop taking your medication without consulting your doctor, even if you feel better. Using your medication correctly will help you keep your blood pressure stable and under control.

It is important to note that each person is unique, and recommendations for blood pressure control may vary depending on individual characteristics and health status. Therefore, regular communication with your doctor and following his or her recommendations are key aspects of preventing and controlling arterial hypertension.
Following these recommendations and making lifestyle changes can significantly reduce your risk of developing hypertension and help you maintain healthy blood pressure.